When it comes to health insurance, you’ll often hear about two main types: private health insurance and public health insurance. Choosing the right type of coverage can be confusing, as both options come with their unique benefits and drawbacks. The choice depends on your specific healthcare needs, financial situation, and the healthcare system in your country.
In this blog post, we will explore the differences between private and public health insurance, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and how to choose the best option for your personal health needs.
What Is Private Health Insurance?
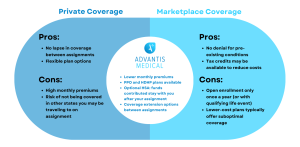
Private health insurance refers to plans offered by private companies. You can obtain private insurance through your employer, purchase it directly from an insurance provider, or acquire it through a marketplace if you’re self-employed or unemployed. Premiums, coverage, and healthcare provider options vary widely depending on the plan you choose.
Key Features of Private Health Insurance:
- Choice of Providers: Private insurance typically offers a broader network of doctors, specialists, and hospitals, giving you more options to choose from.
- Shorter Wait Times: In many cases, private insurance reduces wait times for elective surgeries and specialist appointments.
- Customization: Private health insurance plans often come with options for add-ons or extras, allowing you to customize your coverage to suit specific needs, such as dental, vision, or mental health services.
What Is Public Health Insurance?
Public health insurance is funded and administered by the government. It is designed to provide coverage for a wide population, ensuring access to necessary healthcare services without placing a heavy financial burden on individuals. Examples of public health insurance include Medicare, Medicaid, and national health insurance systems in countries like the UK, Canada, and Australia.
Key Features of Public Health Insurance:
- Lower Costs: Public health insurance usually has lower premiums or no cost at all, as it is funded through taxes or social security contributions.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Most public insurance plans cover a wide range of services, including hospital visits, primary care, and preventive services.
- Universal Access: Public health insurance aims to provide access to healthcare for all citizens, regardless of income level or pre-existing conditions.
Comparing Private and Public Health Insurance
While both types of insurance aim to provide healthcare coverage, they differ in several critical areas, including cost, access to care, and flexibility.
1. Cost
One of the primary differences between private and public health insurance is the cost to the individual.
- Private Health Insurance: Private insurance generally comes with higher premiums, copays, and out-of-pocket expenses. However, it may also offer more comprehensive coverage options and faster access to non-emergency services.
- Public Health Insurance: Public insurance is often more affordable because it’s subsidized by the government. However, some public plans may have longer wait times for specialist appointments and certain procedures due to the high demand for services.
If your primary concern is cost, public health insurance may be the more attractive option. However, if you are willing to pay more for faster service and a wider range of providers, private health insurance may be worth the investment.
2. Access to Providers
Another significant difference is the level of choice you have when selecting healthcare providers.
- Private Health Insurance: Private plans often offer a broad network of doctors, specialists, and hospitals. With private insurance, you typically have the flexibility to see any provider within the network or even outside the network (with higher out-of-pocket costs).
- Public Health Insurance: In public health systems, you may be limited to healthcare providers who participate in the government’s program. The selection of specialists and doctors may be more limited, especially in smaller or rural areas.
If having a wide selection of healthcare providers is important to you, private health insurance provides more options. However, for those comfortable with the available public providers, public health insurance may still offer adequate care.
3. Waiting Times
The speed at which you receive care can also vary significantly between private and public health insurance.
- Private Health Insurance: Private insurance typically provides quicker access to elective procedures and specialist appointments. If you need non-emergency surgery or want to see a specialist without a long wait, private insurance may offer better speed and convenience.
- Public Health Insurance: In public health systems, there can be longer waiting times for non-urgent procedures or specialist care due to the high demand for services. Emergency services, however, are usually prioritized and delivered promptly regardless of the insurance type.
4. Coverage Options
When it comes to coverage, private insurance often allows for more tailored and customizable plans.
- Private Health Insurance: Private insurance offers a wide range of coverage options, allowing you to select a plan that fits your specific healthcare needs. Many private plans include additional benefits like dental, vision, and mental health services, which are not always covered by public plans.
- Public Health Insurance: Public health insurance often focuses on essential medical care, such as hospital stays, surgeries, and doctor visits. While this can cover most needs, there may be fewer options for specialized or supplemental services.
If you’re looking for a plan that covers a wide range of services beyond basic healthcare, private health insurance may be more suitable. However, for those who only need core medical services, public health insurance typically provides sufficient coverage.
Which Is Right for You?
Choosing between private and public health insurance depends on several factors, including your financial situation, healthcare needs, and personal preferences.
Private Health Insurance May Be Right For You If:
- You prefer having more control over your choice of doctors and specialists.
- You want faster access to non-urgent medical procedures.
- You are willing to pay higher premiums for additional services and greater flexibility.
- You have specific healthcare needs that require specialized services or ongoing treatments.
Public Health Insurance May Be Right For You If:
- You are looking for an affordable, comprehensive health plan.
- You don’t mind waiting for non-emergency care.
- You have access to public healthcare providers in your area.
- You want basic health services without high out-of-pocket costs.
Conclusion: Making the Best Choice
Both private and public health insurance have their advantages, and the best choice depends on your individual needs. Private insurance offers more flexibility and faster access to care, but comes with higher costs. Public insurance provides more affordable coverage with a focus on essential medical services, though you may face longer wait times.
Ultimately, the decision between private and public health insurance should be based on your budget, healthcare preferences, and access to healthcare providers in your region. By weighing the pros and cons of each option, you can make an informed decision that suits your health and financial needs.